This blog is meant for people who are new to Big-O Notation or people who need a refresher on what Big-O Notation is. If you don't need this this bigo cheatsheet, might be more up your alley. It covers common data structure operations and array sorting algorithms.
What is Big O Notation
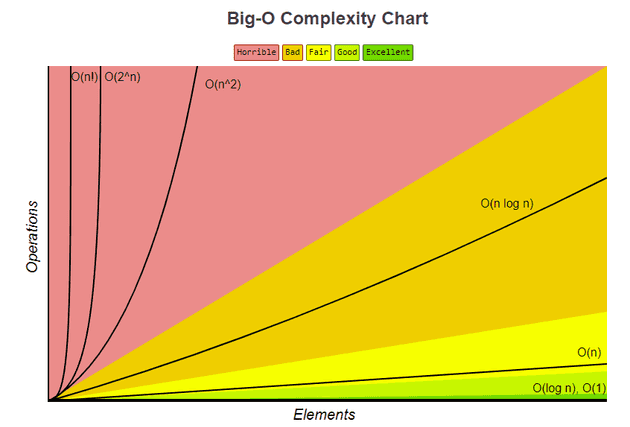
Big O notation is a method to tell how fast a algorithm is, this is done my tracking the operations or steps it takes to get to the solution. This lets us to account for different clock speeds on CPUs. A algorithm is not measured in seconds, but in terms of growth of the algorithm.
Algorithms?
Algorithms are just steps to change your current situation into a desired outcome. It can be anything from a instructions for a sandwich to ChatGPT. Algorithms are something integral to software development. Big O notation came along so people can discuss Algorithms and the differences between them.
For example
#include <stdio.h>
int search(int arr[], int arrSize, int value){
// loop thru everyElement to find the index value
// if it exists in the array
for(int i = 0; i < arrSize; i++){
if(arr[i] == value){
return i;
}
}
// return -1 if not found
return -1;
}
int main() {
int arr[10] = {0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9};
int found = search(arr,10, 9);
printf("Found at %d",found);
return 0;
}The Big O runtime for the code above would be O(n). The search function is a linear algorithm. It checks the array one by one until it finds the value it's looking for or until it searches the entire array. While the best case for this function is when it finds the value right way, this is not how we get the Big O runtime of a function. We must calculate it when looking at the worst possible runtime.
Does performance matters?
With a small enough input or fast enough CPU then you many not need a better algorithm for your use-case, whats 50ms or 7ms to a person. Anything under 100ms is instantaneous to most people, if this blog is to be believed: How Fast is Real-Time? Human Perception and Technology.
So when do you need to bother with better algorithms?
When performance matters
| Algorithms | Elements | Steps | runtime |
|---|---|---|---|
| Linear Search | 100 steps | 100 steps | 100ms |
| Linear Search | 10000 steps | 10000 steps | 11 days |
| Binary Search | 100 steps | 7 steps | 7ms |
| Binary Search | 10000 steps | 14 steps | 14ms |
For small enough inputs any algorithm can be ad good as any other, but when inputs begin to grow things can change rapidly. From the table above we can see two algorithms solving the same problem, one can take days while the other can be instantaneous.
What is a binary search
#include <stdio.h>
int binarySearch(int arr[], int arrSize, int value){
// eliminate half the elements each iteration
int lower = 0;
int upper = arrSize;
int mid;
while(lower <= upper){
mid = lower + (upper - lower)/2;
if(arr[mid] == value){
return mid;
}else if(arr[mid] < value){
lower = mid + 1;
}else{
upper = mid - 1;
}
}
// return -1 if not found
return -1;
}
int main() {
int arr[10] = {0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9};
int found = binarySearch(arr,10, 9);
printf("Found at %d",found);
return 0;
}A binary search as Big O runtime of O(Log(n)). It works by dividing the array into in half until you find narrow down the location of the value you are searching for. To be able to use this algorithm then the array needs to be sorted. This lets the algorithm know which half of the array could have the number it is looking for. Looking at the above example, if you are looking for the number 9. If you check the middle of the array and see 5. Then you know you just need to look at the right half of the array since all values to the left of 5 are less than it.
Time Complexity vs Space Complexity
Big O notation is not justed used when discussing how fast a algorithms is, it can also be used when discussing how memory efficient algorithms are. For example if you are tasked with sorting an array of numbers do you create a new array or sort the elements in the original array. If you make a copy of the array then your algorithm would have a space complexity of O(n). If you sorted the array in place without making a copy then your algorithm would have a space complexity of O(1) also known as constant space complexity.
Inconsistent naming
Depending on what part of the internet you are one, then Big O runtime more commonly referred by time complexity. Some people also say Big O space instead of Big O space. This is kinda like the tab vs space thing between programmers. Do with this information what you will.
Trade offs with time and space
Sometimes when making algorithm you will need to consider whats more important, the runtime or how much memory your algorithm can use.
For example
#include <stdio.h>
int getSum(unsigned int value){
int sum = 0;
while(value !== 0){
sum += value;
value--;
}
// return -1 if not found
return sum;
}
int main() {
int result = getSum(10);
printf("result %d:",result);
return 0;
}The function getSum has a time complexity of O(n) and a space complexity of O(1). There is a way do this in constant time, since the number must be a positive number then we can make a array with all the possible solutions as elements and use the input as the index to get the right value. This method would have a Time complexity of O(1) and a space complexity of O(n) since we build an array to size N. Each solution could be good depending if space is costly than time is in your use-case.
Anytime a function as a int as a input, then you could use this method.
By the way, this problem does have a formula for constant time and space complexity. It's called Sum of Integers Formula
S = n(a + l)/2- S = sum of the consecutive integers
- n = number of integers
- a = first term
- l = last term
Recap
- Algorithms are not measured in speed
- Algorithms are measured in growth
- Algorithms times are written in Big O notation
- Big O runtime is always the worst-case